What is Huntington’s disease?
Huntington’s disease is a genetic condition that affects the cells in your brain. It’s a progressive condition that gets worse over time. Common symptoms affect your movement, thoughts and feelings. Symptoms usually start between the ages of 30 and 50. Treatment is available to help you feel more comfortable.
What is Huntington’s disease?
Huntington’s disease is an inherited condition that causes brain cells to slowly lose function and die. It affects the cells in parts of your brain that regulate voluntary movement and memory. Common symptoms include uncontrollable movements and changes to your thinking, behavior and personality. These symptoms get worse over time.
What are the types of Huntington’s disease?
There are two types of Huntington’s disease:
- Adult onset: This is the most common form. Symptoms usually begin after age 30.
- Early onset (juvenile Huntington’s disease): Early onset affects children and teenagers. It’s very rare.
How common is Huntington’s disease?
Huntington’s disease affects an estimated 3 to 7 out of every 100,000 people, most often people of European ancestry (biological family comes from European descent).
Related Topics (ads):
What are the symptoms of Huntington’s disease?
Huntington’s disease affects you both physically and mentally. Physical symptoms include:
- Uncontrolled movements like jerking or twitching (chorea).
- Loss of coordination (ataxia).
- Trouble walking.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
- Slurred speech.
Physical symptoms may start in small ways — for example, difficulty holding a pen, clumsiness or losing balance — and then get worse over time.
In addition, if you have Huntington’s disease, you may develop:
- Emotional changes like mood swings, depression and irritability.
- Problems with memory, focus and multitasking.
- Trouble learning new information.
- Difficulty making decisions and reasoning.
Your physical and mental symptoms may not affect your daily life much at first. But over time, these symptoms will make your usual tasks more difficult to do on your own.
What is Huntington’s disease chorea?
One of the first physical symptoms of Huntington’s disease is chorea. Chorea is unintended jerks or twisting movements. Chorea usually affects your hands, fingers and facial muscles first. Later, it also makes your arms, legs and torso move uncontrollably. Chorea can make speaking, eating and walking more difficult. It may affect your ability to perform everyday activities, such as driving, as well.
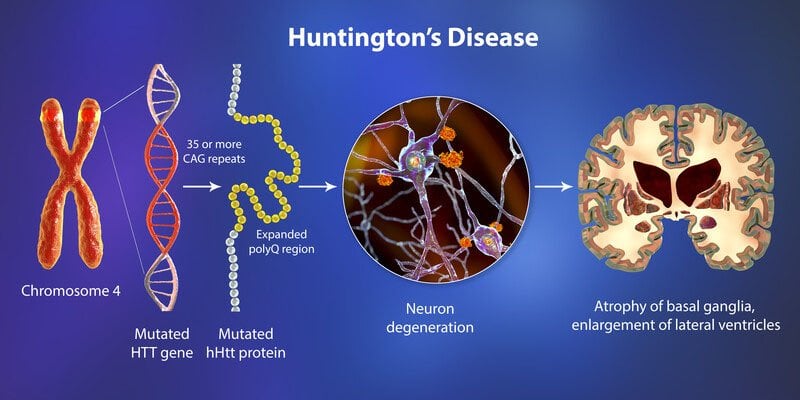
What causes Huntington’s disease?
A genetic change (mutation) of the HTT gene causes Huntington’s disease. The HTT gene makes a protein called huntingtin. This protein helps your nerve cells (neurons) function.
If you have Huntington’s disease, your DNA doesn’t have all the information needed to make the huntingtin protein. As a result, these proteins grow in an abnormal shape and destroy (instead of help) your neurons. Your neurons die because of this genetic mutation.
The destruction of nerve cells happens in the basal ganglia or the region of your brain that regulates your body’s movements. It also affects the brain cortex (surface of your brain) that regulates your thinking, decision-making and memory.
Is Huntington’s disease inherited?
Yes, you can inherit the genetic change (mutation) that causes Huntington’s disease. You can develop this condition if one of your biological parents carries the genetic change and passes it on to you. This is an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. In rare cases, the genetic change happens without any history of the condition in your biological family.
What are the risk factors for Huntington’s disease?
Anyone can develop Huntington’s disease, but it’s most common if someone in your biological family has the condition. If one of your parents has Huntington’s disease, you have a 50% chance of also developing it.
What are the complications of Huntington’s disease?
Huntington’s disease is a progressive condition. This means that your symptoms get worse over time. Complications could include worsening symptoms, like:
- Dementia (loss of brain function, memory loss, personality changes).
- Physical injury from involuntary movements or falls.
- Difficulty swallowing, eating or drinking (malnutrition).
- Inability to walk without assistance.
- Infections (pneumonia).
Children diagnosed with juvenile Huntington’s disease may experience seizures.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is Huntington’s disease diagnosed?
A healthcare provider, like a neurologist (a doctor specializing in the brain and nerves), will diagnose Huntington’s disease after performing a physical exam and a neurological exam. They’ll look for symptoms of the condition that affect your movements, like twitches and jerking, as well as problems with your balance, reflexes and coordination. Your neurologist will also want to know if anyone else in your biological family has the condition. Often, you’ll need a genetic test to confirm the diagnosis.
Tests can rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms and confirm a Huntington’s disease diagnosis. Tests include:
- Blood tests.
- Genetic testing.
- Imaging tests (magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scan).
What is genetic testing to diagnose Huntington’s disease?
A genetic test is a blood test that looks for changes to your DNA. Your healthcare provider draws a sample of your blood and sends it to a lab to look at your DNA. The test determines if you have a genetic change in the HTT gene. A genetic counselor (someone who specializes in genetic testing) will discuss the process and results with you.
Your provider may also ask if your biological family members can come in for genetic testing, too. This can help assess their risk of developing the condition or having a future child with the condition.
Can you find out if you have Huntington’s disease before symptoms appear?
Yes. If one of your parents or siblings has Huntington’s disease, your risk of having it is high. Predictive genetic testing — testing for genetic conditions before symptoms start — can tell if you have the gene change that causes Huntington’s disease.
People have different responses to learning about a condition they’ll get someday. Knowing about the gene could help you make family plans and financial decisions. But it could also be emotionally difficult, especially since you can’t prevent the condition. It’s essential to discuss testing with your genetic counselor to see whether finding out early is the best decision for you.
Management and Treatment
How is Huntington’s disease treated?
Huntington’s disease treatment focuses on helping you feel more comfortable. There isn’t treatment available to stop, slow or prevent symptoms. Because this condition affects your physical, mental and emotional health, you may need several types of treatment, including:
- Physical therapy or occupational therapy.
- Speech therapy.
- Counseling.
- Medications.
What medications treat Huntington’s disease?
Your healthcare provider may prescribe different medications to address your symptoms. To treat chorea, common medications include:
- Tetrabenazine (Xenazine®).
- Deutetrabenazine (Austedo®).
- Haloperidol (Haldol®).
To manage emotional symptoms, your healthcare provider may recommend:
- Antidepressants like fluoxetine and sertraline.
- Antipsychotic medications like risperidone and olanzapine.
- Mood-stabilizing medications like lithium.
Are there side effects of the treatment?
Each type of treatment comes with possible side effects. For example, physical therapy may cause muscle soreness, and medications to treat chorea may cause fatigue or low blood pressure. Your healthcare provider will explain these to you before you begin treatment so you can make an informed decision about your health.
Who is on my care team?
Your care team may include the following healthcare providers:
- A neurologist.
- A psychiatrist.
- A genetic counselor.
- A physical therapist.
- An occupational therapist.
- A speech therapist.
Prevention
Can Huntington’s disease be prevented?
There’s no known way to prevent or reduce your risk of Huntington’s disease. If you’re planning on expanding your family, talk to a genetic counselor about genetic testing to understand your chances of having a child with a genetic condition. It’s possible to do in vitro fertilization (IVF) with genetic testing to make sure you don’t pass Huntington’s disease on to your future children.
Outlook / Prognosis
How does Huntington’s disease progress?
Huntington’s disease is a progressive condition. This means it slowly gets worse over time. The way the condition progresses varies for each person, but may include:
- Early stage: Symptoms are mild. You might feel moody or clumsy and struggle with complex thinking. You may also have small, uncontrollable movements, but typically, you can continue your everyday activities.
- Middle stage: Physical and mental changes make working, driving and household chores very difficult. You may have trouble swallowing, which can make speaking and eating meals challenging but not impossible. Your balance may be off, increasing your risk of falling. You can still manage your personal care like bathing and getting dressed.
- End stage: Completing daily tasks is hard to do on your own. Most people aren’t able to get out of bed without help. You’ll need around-the-clock care during this stage, especially to eat, bathe and monitor your health and well-being.
Is there a cure for Huntington’s disease?
There’s no cure for Huntington’s disease. However, clinical trials (tests in people) are ongoing to learn more about the condition and how newer treatments can help.
What is the life expectancy for Huntington’s disease?
The average lifespan after a Huntington’s disease diagnosis is 10 to 30 years.
Is Huntington’s disease fatal?
Huntington’s disease itself isn’t fatal. The condition makes everyday activities more difficult to do over time. How fast it progresses varies from person to person. But you can die from its complications, such as infections like pneumonia or injuries related to falls.
Living With
How do I take care of myself?
You can take several steps to have the best possible quality of life as Huntington’s disease progresses. Here are some suggestions:
- Get regular exercise: Research shows exercise helps you feel better overall.
- Eat healthy foods: Your healthcare provider might recommend changes to your nutrition intake. Involuntary movements can burn up to 5,000 calories a day.
- Drink plenty of water: Dehydration is a risk when you have trouble swallowing. Your healthcare provider might recommend that you take steps to stay hydrated.
- Find a support group: Ask your healthcare provider for community resources where you can connect with others.
- Research care services: At some point, you’ll need a high level of care from either home care services or a nursing home.
- Appoint a trusted advisor: As the condition progresses, you’ll have to pass financial duties and decision-making on to someone else. This is an important and difficult decision to make. Make sure you organize your expectations before your symptoms make decision-making difficult.
Remember, although you can’t prevent Huntington’s disease, you can plan for it. Symptoms take years to worsen. That gives you time to find healthcare providers you trust and get the support you need for the future. If you or someone in your family has Huntington’s disease, talk with a genetic counselor about what you need to know.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
- What’s my prognosis?
- What type of treatment do you recommend?
- What side effects from treatment should I look for?
- How do I prevent complications?
- How should I prepare for end-stage Huntington’s disease?
- Do you recommend genetic testing for others in my family?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Huntington’s disease makes it harder for you to take care of yourself over time. It can be extremely difficult to learn you or a loved one has this condition. Since symptoms take years to progress, you have time to prepare for full-time care and assistance. While you need to make important long-term decisions about your health, you don’t need to rush into these decisions that can affect your future.
It can be easy to give up hope after learning about how this condition can affect you later on, but you’re not alone. Many people find comfort in speaking with a mental health professional or joining a support group. Research is also ongoing to learn more about treatment options to help improve your quality of life.